How Do I Distinguish Between Septal Bulge And Regular Back Pain?
Normal back pain usually disappears within a few hours or after rest, while the symptoms of interstitial bulge can continue for days or weeks.
Back pain is one of the most common ailments: it affects up to eight out of ten people at some point in their lives. Many different things can lead to back pain and tenderness, as well as how long and how intense the pain feels.
Most cases are mild and go away on their own after rest and exercise. Often, however, back pain recurs and can cause chronic problems that require more planning and attention.
Often people ignore back pain and symptoms, and imagine them to be momentary and transient. However, back symptoms should be addressed immediately, as rapid treatment can prevent the development of deeper problems. Sometimes back pain can be a sign of a more serious problem.
The bulge of the septum is one of the back problems that people often ignore and think it is just plain back pain. However, the bulge in the septum causes severe symptoms within a few days and becomes more difficult to treat.
For this reason, it is important to know what distinguishes between ordinary back pain and the more severe septal bulge.
What is a septal bulge?
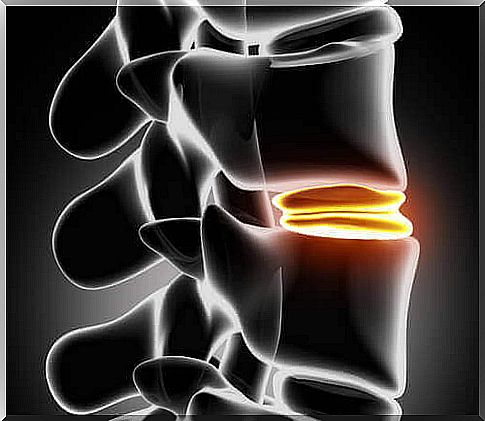
The spine is separated by a cushioned formation designed to protect the vertebrae from damage and shock. The pillows also protect the nerves in the spine so they don’t get pinched.
The soft composition of the spacers facilitates the mobility of the spine and allows the spine to curve and bend. Over the years, the spacers lose some of their mobility and are no longer as stretchy as when they were young. At the same time, the weakening of the spacer begins and the possibility of the spacer moving away from places caused by unexpected movements increases. The pain caused by the bulge in the septum is due to the soft contents of the septum bulging in the direction of the spinal canal, where it causes compression of the nerve roots and radiation pain.
In severe cases, the shims may rupture if exposed to severe impact or injury.
Usually, the bulge in the septum causes severe pain on one side of the body and is accompanied by numbness, muscle weakness, and difficulty moving. Diagnosis is often made by magnetic resonance imaging.
How to distinguish between back pain and septal bulge?

The bulging of the septum usually causes pain that slowly worsens. Often the pain is mixed with normal back pain, at least initially.
In order to be able to distinguish the pain caused by the bulge of the septum from the back pain, it is important to know that the pain caused by the bulge of the septum increases, for example, when coughing, during stretching and after long sessions.
In general, the pain is relieved if you lie on your back with your feet hooked or walking instead of standing. The bulge in the septum often causes a feeling of weakness in the other leg due to nerve compression. The same does not happen with normal back pain. Back pain can be disgusting, but it does not affect muscle function or cause a feeling of numbness.
If you suffer from chronic pain caused by a bulge in the septum, the health of the spine may be at risk. At worst, severe bulging of the septum can cause urinary and fecal incontinence, as well as numbness of the urethra and anal area. This condition is called cauda equina . Cauda equina is a serious condition and requires immediate medical evaluation.
The most obvious symptom of interstitial bulge is long-lasting pain that is not relieved by resting. Normal back pain usually worsens at rest and improves within a few days.
What to do if you suspect a bulge in the septum
If you suspect a bulge in the septum and suffer from the symptoms mentioned in this article, you should make an appointment with your doctor immediately. Your doctor may prescribe you for magnetic resonance imaging, where the bulge in the septum can be confirmed.
In some cases, surgery is required, but often the bulge can be treated with exercise and stretching, as well as improving muscle condition. Back strengthening exercises are an important part of treating septal bulge. Physiotherapy can also be a significant help.
Many patients with interstitial bulge also try a variety of alternative therapies, such as:
- Heat therapy
- Electrotherapy
- Pressure treatment
- Massage
- Hydrotherapy
- Natural painkillers
These therapies can relieve pain and improve back mobility and muscle strength. You can also relieve pain with the following tips:
- Sleep with a good, sturdy mattress that helps prevent back problems. Try different mattresses and ask for recommendations from vendors and back experts. Do not sleep on too soft a surface.
- Sleep in the fetal position and place a pillow between your knees. This prevents the pelvis from twisting.
- Avoid sleeping on your stomach, this will strain your back.
- Rest for a few hours during the day if your back pain is severe. However, do not stay in bed all day. Exercise is an important part of recovery and back pain relief. Exercise light exercise, avoid strenuous exercise and sudden movements.
- Do not lift heavy objects, and move prudently and carefully.
- Walk or swim for 30 minutes a day, even after the pain is gone. Regular exercise and back exercise will help prevent trouble from recurring.